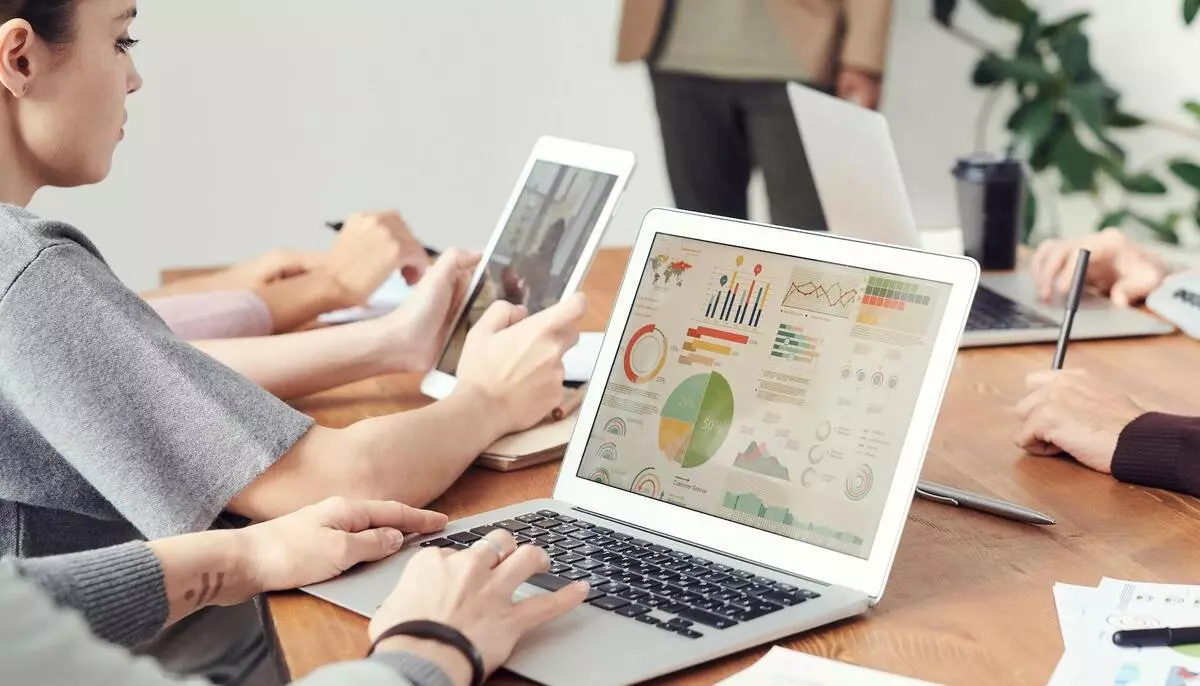
What is Financial Analyst?
A financial analyst is a professional who plays a key role in analyzing financial data and providing insights and recommendations to individuals, companies, or institutions regarding their financial decisions. Financial analysts work across various sectors, including corporate finance, investment banking, asset management, and financial planning, to help clients make informed choices about investments, budgeting, and other financial strategies.
One of the primary responsibilities of a financial analyst is to conduct in-depth financial analysis. They examine financial statements, income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to assess the financial health and performance of companies or investment opportunities. By analyzing historical data and market trends, financial analysts identify patterns and factors that may impact future financial performance.
Financial modeling is a crucial aspect of a financial analyst's role. They create financial models to forecast future cash flows, assess the potential risks and returns of investments, and evaluate the financial impact of different scenarios. Financial modeling enables analysts to make accurate projections and simulations, aiding clients in making well-informed financial decisions.
Moreover, financial analysts monitor economic indicators, market trends, and regulatory changes that may affect financial markets and investments. They stay up-to-date with industry developments, changes in interest rates, and geopolitical events to provide timely and relevant insights to clients. Being well-informed about market conditions helps financial analysts tailor their recommendations to specific client needs and objectives.
Effective communication is essential for financial analysts as they need to convey complex financial information to clients and stakeholders. They produce reports, presentations, and investment recommendations that are clear, concise, and tailored to their audience. Good communication skills help clients understand the rationale behind investment decisions and build trust between the analyst and the client.
Financial analysts often work in financial institutions, investment firms, or as independent consultants. They play a crucial role in providing financial advice and guiding clients in making strategic financial decisions. By applying their financial analysis skills, industry knowledge, and communication abilities, financial analysts assist clients in achieving their financial goals, managing risk, and optimizing their financial performance. Their expertise is invaluable in navigating the complexities of the financial landscape and ensuring that clients' financial decisions are well-grounded and aligned with their long-term objectives.
“ Financial Analysts utilize data analytics to analyze financial data, assess investment opportunities, and create financial models. Your skills will be instrumental in aiding financial planning and guiding investment decisions.”
The most important things to consider
Financial Analysis Skills: Financial analysts must possess strong financial analysis skills, including proficiency in financial modeling, forecasting, and data analysis. They use these skills to examine financial statements, assess company performance, and identify trends and opportunities in financial markets. Financial analysis is the foundation of their work, enabling them to make informed recommendations and decisions related to investments, budgeting, and financial planning.
Industry Knowledge and Research: Financial analysts need to have a deep understanding of the industries and markets they operate in. They stay up-to-date with economic trends, industry developments, and regulatory changes that may impact financial decisions. Conducting thorough research on companies, sectors, and economic indicators allows financial analysts to provide valuable insights to clients and stakeholders, guiding them in making strategic financial decisions.
Communication and Presentation Skills: Effective communication is essential for financial analysts as they often interact with clients, executives, and other stakeholders. They must be able to articulate complex financial concepts and analysis results in a clear and understandable manner. Whether through written reports, presentations, or verbal discussions, strong communication skills help financial analysts build trust and credibility with their audience, ensuring that their financial recommendations are well-received and acted upon.
- Salary Low: $52,888.00
- Salary High: $126,918.00
- Education Needed: Bachelor's

Job Duties
- Evaluate financial risks, prepare financial forecasts, financing scenarios and other documents concerning capital management, and write reports and recommendations
- Plan short- and long-term cash flows and assess financial performance
- Analyze investment projects
- Advise on and participate in the financial aspects of contracts and calls for tender
- Follow up on financing projects with financial backers
- Develop, implement and use tools for managing and analyzing financial portfolio
- Prepare a regular risk profile for debt portfolios
- Assist in preparing operating and investment budgets
- Develop and update financial or treasury policies
- Collect financial and investment information about companies, stocks, bonds and other investments using daily stock and bond reports, economic forecasts, trading volumes, financial periodicals, securities manuals, company financial statements and other financial reports and publications
- Examine and analyze financial and investment information collected, including profiles of companies, stock and bond prices, yields and future trends and other investment information
- Provide investment advice and recommendations to clients, senior company officials, pension fund managers, securities agents and associates
- Prepare company, industry and economic outlooks, analytical reports, briefing notes and correspondence
Employment Requirements
- A bachelor's degree in commerce, business administration, accounting, finance or economics and on-the-job training and industry courses and programs are usually required.
- A master's degree in business administration (MBA) (concentration in finance) or in finance may be required.
- The Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, available through a program conducted by the CFA Institute or an other recognized financial designations (CFP, CIM or others), is usually required.
- Other designations, such as Chartered Professional Accountant (CPA) and Certified Treasury Professional (CTP), may be required by some employers.