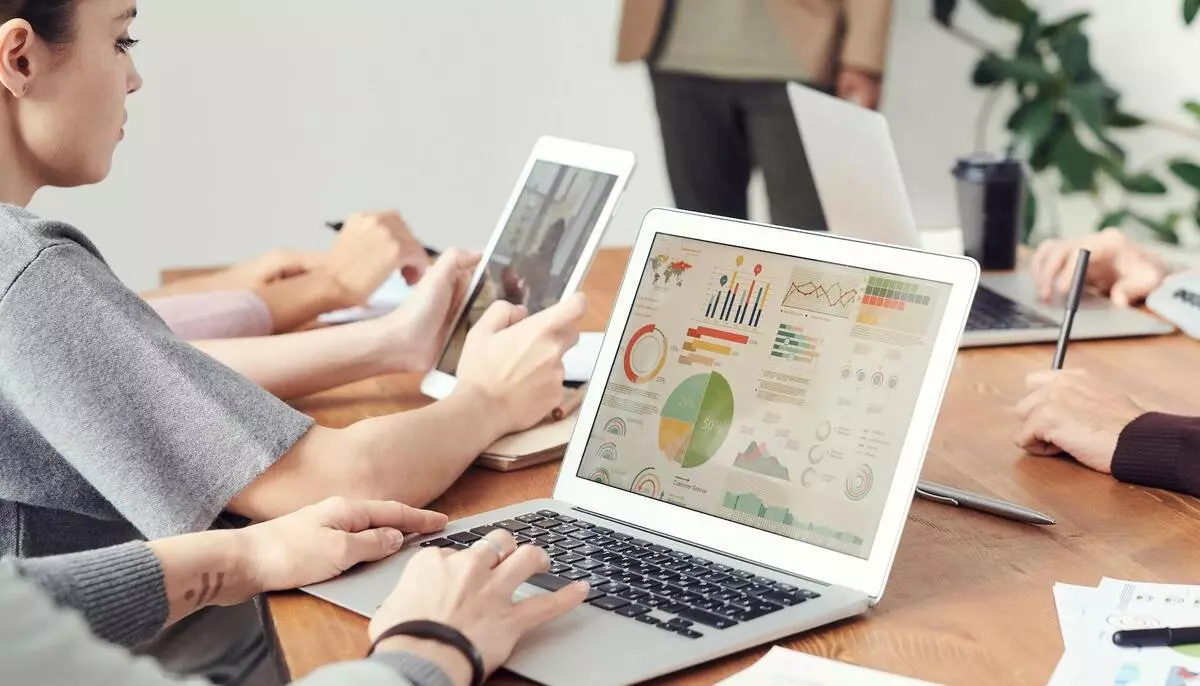
What is Operations Analyst?
An operations analyst is a professional responsible for analyzing and optimizing various operational processes within an organization. These analysts work across diverse industries and sectors, focusing on enhancing efficiency, productivity, and cost-effectiveness of business operations. Their primary objective is to identify areas for improvement, streamline workflows, and implement strategies that lead to enhanced performance and overall organizational success.
One of the key responsibilities of an operations analyst is to conduct in-depth analysis of operational data. They gather and analyze information related to processes, performance metrics, resource utilization, and workflow bottlenecks. By employing statistical techniques and data visualization tools, operations analysts identify trends, patterns, and areas of inefficiency that require attention.
Financial analysis is also an essential aspect of an operations analyst's role. They evaluate the financial impact of operational changes and identify cost-saving opportunities. Operations analysts often collaborate with finance teams to create budgeting and forecasting models, ensuring that operational improvements align with the organization's financial goals and objectives.
Moreover, operations analysts work closely with cross-functional teams, including production, supply chain, logistics, and customer service, to understand their unique operational challenges and requirements. They facilitate communication and collaboration among these teams to implement process improvements and drive continuous improvement initiatives throughout the organization.
Effective communication is vital for operations analysts as they need to present their analysis findings and recommendations to various stakeholders, including management and department heads. They produce reports, presentations, and action plans that are clear, concise, and data-driven, enabling decision-makers to understand the rationale behind operational improvements and make informed choices.
In addition to data analysis and communication skills, operations analysts must be proficient in project management. They often oversee the implementation of operational changes and monitor their impact over time. By managing projects and coordinating with different teams, operations analysts ensure that process improvements are successfully integrated into daily operations and deliver the expected outcomes.
“ Operations Analysts optimize processes and efficiency using data analysis. Your ability to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement will enhance business operations and reduce costs.”
The most important things to consider
Data Analysis and Problem-Solving Skills: Operations analysts must possess strong data analysis skills and the ability to interpret complex data sets related to operational processes. They use statistical methods, data modeling, and visualization techniques to identify patterns, trends, and inefficiencies. By analyzing the data, they can pinpoint areas for improvement and propose data-driven solutions to enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Process Optimization and Continuous Improvement: Operations analysts play a critical role in optimizing and streamlining operational processes. They evaluate existing workflows, identify bottlenecks, and suggest improvements to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Emphasizing continuous improvement, operations analysts monitor the implementation of changes and assess their impact over time, ensuring that the organization sustains and builds upon the improvements made.
Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration are vital for operations analysts as they work with cross-functional teams and stakeholders. They need to effectively communicate their analysis findings, insights, and recommendations to management and department heads. Collaborating with various teams, including production, logistics, and customer service, helps ensure that proposed solutions align with the organization's overall objectives and are implemented successfully.
- Salary Low: $66,946.00
- Salary High: $161,326.00
- Education Needed: Graduate

Job Duties
- Conduct research to extend mathematical knowledge in traditional areas of mathematics such as algebra, geometry, probability and logic
- Apply mathematical techniques to the solution of problems in scientific fields such as physical science, engineering, computer science or other fields such as operations research, business or management
- Conduct research into the mathematical basis of the science of statistics
- Develop statistical methodology and advise on the practical application of statistical methodology
- Apply statistical theory and methods to provide information in scientific and other fields such as biological and agricultural science, business and economics, physical sciences and engineering, and the social sciences
- Apply mathematical models to forecast and calculate the probable future costs of insurance and pension benefits
- Design life, health, and property insurance policies, and calculate premiums, contributions and benefits for insurance policies, and pension and superannuation plans
- May assist investment fund managers in portfolio asset allocation decisions and risk management. They also use these techniques to provide legal evidence on the value of future earnings
Employment Requirements
- Mathematicians and statisticians usually require a graduate degree in mathematics or statistics.
- Actuaries usually require post-secondary education in actuarial science, mathematics, statistics, economics, commerce or business administration.
- Actuaries are conferred fellowships through the Canadian Institute of Actuaries upon successful completion of professional examinations and three years of work experience in the actuarial field as an actuarial assistant or in a related position.